A tooth infection may start as a minor inconvenience—perhaps a little swelling, pain, or sensitivity—but ignoring it can have severe consequences. Many people underestimate the dangers of a tooth infection, assuming it will heal on its own. Unfortunately, untreated dental infections can escalate, spread to other parts of the body, and become life-threatening. While the exact timeline for a tooth infection to turn fatal varies, the risks increase with every passing day without proper treatment.
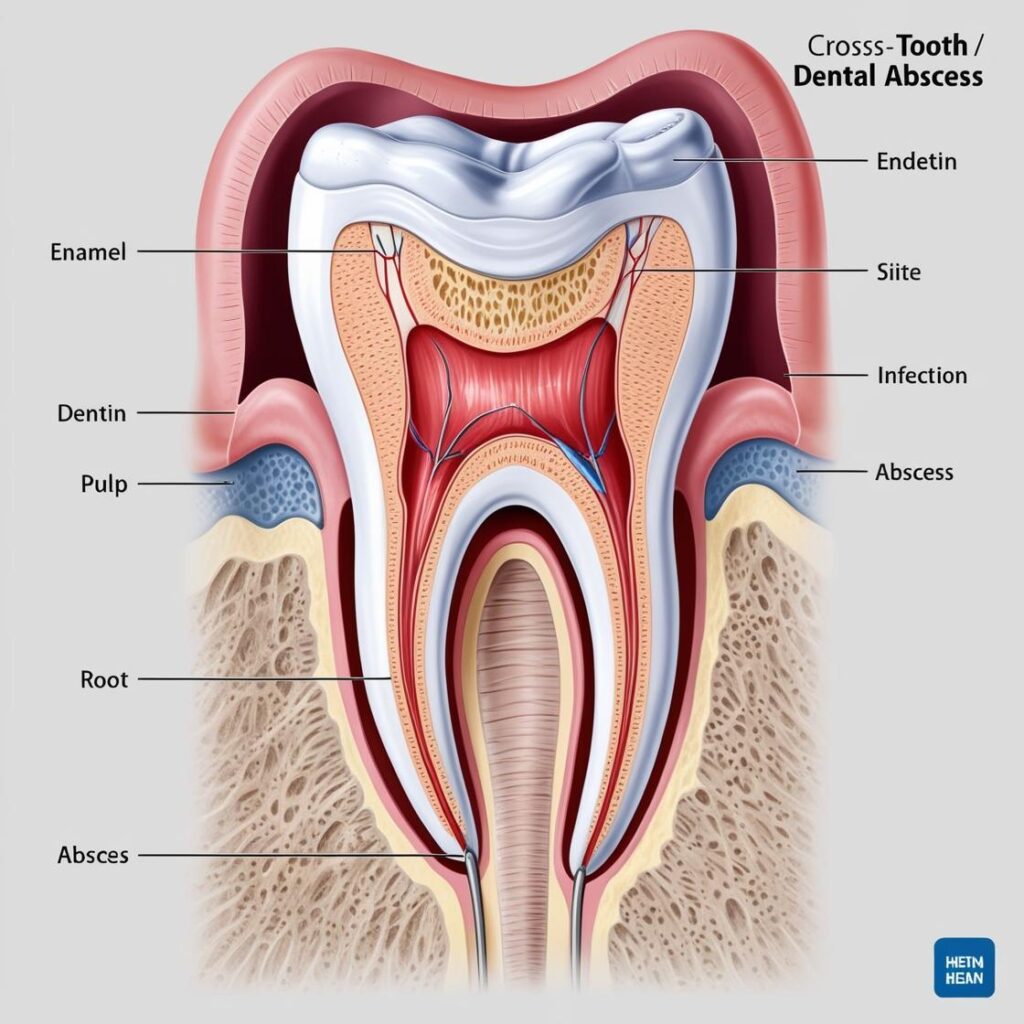
What Causes a Tooth Infection?
A tooth infection, often referred to as a dental abscess, occurs when bacteria enter the tooth’s inner pulp. This can happen due to untreated cavities, cracks, injuries, or gum disease. The pulp, which contains blood vessels and nerves, becomes inflamed and filled with pus as the body tries to fight off the infection.
Imagine a small leak in a pipe. If ignored, the water begins to flood the surrounding area, damaging everything in its path. Similarly, a tooth infection can start small but gradually spread to the jaw, sinuses, and even vital organs if left untreated.
How Quickly Can a Tooth Infection Spread?
The timeline for a tooth infection to become dangerous depends on several factors, including the individual’s immune system and the location of the infection. In some cases, complications can arise within days, especially if the bacteria spread to critical areas like the throat, bloodstream, or brain. For others, the infection may linger for weeks before turning life-threatening.
For instance, an upper tooth infection can spread to the sinuses or even the brain, while an infection in the lower jaw can impact the throat and airways, potentially obstructing breathing. The longer treatment is delayed, the higher the risk of severe complications.
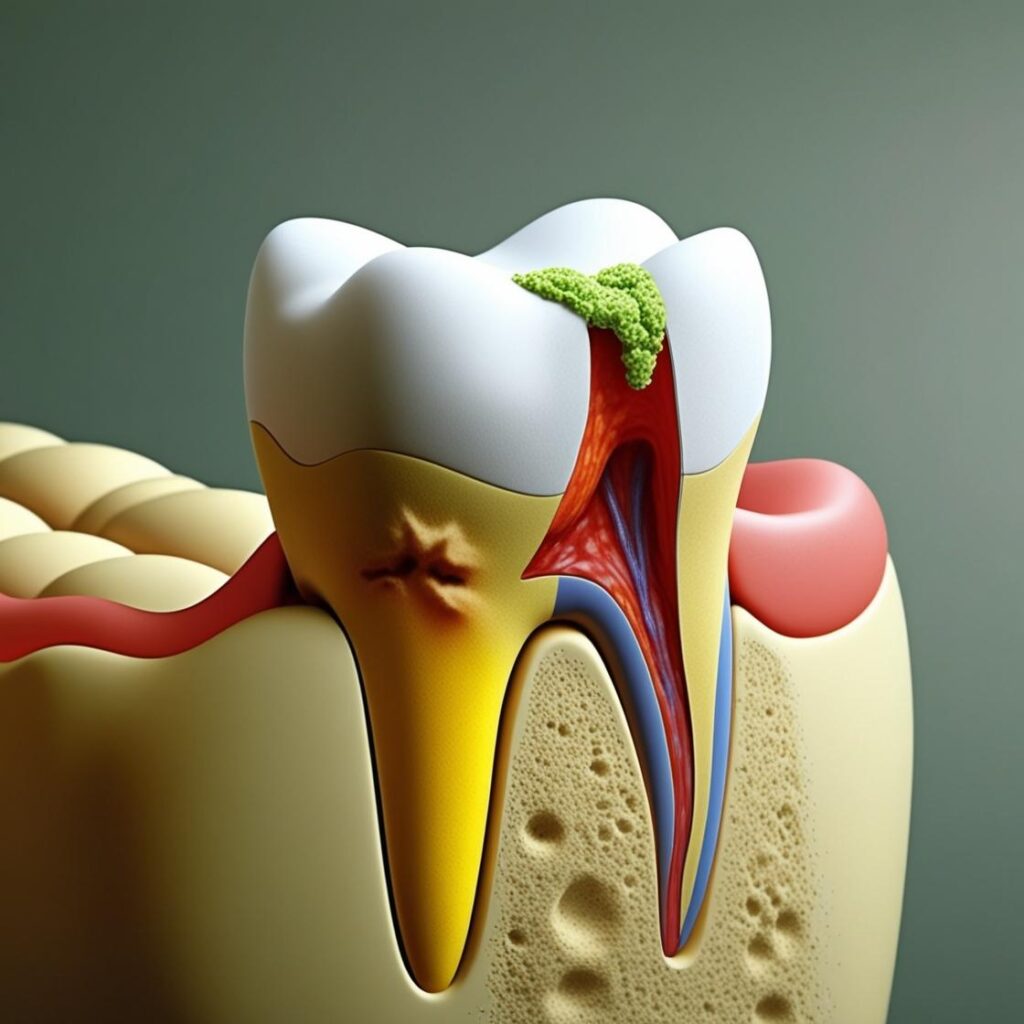
The Dangers of Ignoring a Tooth Infection
If left untreated, a tooth infection doesn’t just stay confined to the tooth. Here are the most serious complications that can arise:
1. Sepsis: A Silent Killer
One of the most dangerous outcomes of a dental infection is sepsis, a life-threatening condition where the body’s immune response to an infection spirals out of control. When bacteria from the infected tooth enter the bloodstream, they can travel to various organs, causing widespread inflammation and organ failure. Sepsis often begins with symptoms like fever, chills, and rapid breathing but can quickly progress to confusion, a drop in blood pressure, and even death if not treated promptly.
2. Airway Obstruction
Infections in the lower jaw can lead to swelling in the floor of the mouth or throat, a condition known as Ludwig’s angina. This swelling can obstruct the airway, making it difficult or impossible to breathe. It’s a medical emergency that requires immediate attention.
3. Brain Abscess or Meningitis
Although rare, a tooth infection can spread to the brain, causing a brain abscess or meningitis. These conditions are particularly dangerous because they can result in permanent neurological damage or even death. Early symptoms include severe headaches, fever, and confusion.
Early Warning Signs You Should Never Ignore
Recognizing the signs of a tooth infection early can prevent it from escalating into a life-threatening condition. Common symptoms include:
- Persistent, throbbing pain that doesn’t go away.
- Swelling in the gums, face, or jaw.
- A foul taste in the mouth or bad breath.
- Fever, chills, or fatigue.
- Difficulty opening your mouth, swallowing, or breathing.
If any of these symptoms occur, particularly difficulty breathing or swallowing, it’s crucial to seek emergency medical attention.
Treatment Options for a Tooth Infection
Once a tooth infection is diagnosed, timely treatment is essential. Dentists typically begin by controlling the infection and addressing the root cause. Treatments may include:
- Antibiotics: These help fight the infection and prevent it from spreading to other parts of the body.
- Draining the Abscess: The dentist may make a small incision to drain the pus and relieve pressure.
- Root Canal: A root canal procedure removes the infected pulp while saving the tooth.
- Tooth Extraction: In severe cases where the tooth cannot be saved, it may need to be removed to stop the spread of infection.
Ignoring treatment can lead to complications that require hospitalization and intensive care, such as intravenous antibiotics or surgical intervention.
Prevention is the Best Cure
To avoid the risks of a tooth infection altogether, maintaining good oral hygiene is key. Brush your teeth twice a day with fluoride toothpaste, floss daily, and schedule regular dental checkups. Treat cavities, cracks, or gum disease promptly to prevent bacteria from gaining a foothold.
Think of your teeth as a car engine. Routine maintenance, like oil changes, ensures it runs smoothly. Neglecting small issues, like a minor leak, can lead to complete engine failure. Similarly, small dental problems can escalate into major health crises if ignored.
While a tooth infection may not seem dangerous at first, it can escalate into a life-threatening emergency if left untreated. Complications like sepsis, airway obstruction, and brain infections are rare but very real risks. The timeline for these outcomes varies, but the key takeaway is this: the longer you wait to treat a tooth infection, the greater the danger.
If you suspect a tooth infection, don’t delay. Seek professional dental care immediately to prevent small problems from turning into life-threatening ones. Early intervention not only saves your tooth but also protects your overall health. Remember, when it comes to infections, time is of the essence.
















